Arsip Blog
Minggu, 19 Februari 2017
EXAMINATION : ELECTRICAL AUTOMATION
1. PT-100 sensors are some times used with 3 or even 4 wires. What is the reason for this?
Higher measuring accuracy.
2. In the diagram below we want to verify the resistance of the PT100 sensor. What is the correct calculation?
R(Pt100) = R1 - R2
3. In some cases we can see that a resistor is connected over an alarm contact (see diagram). Why is this connection used?
To monitor the cable/wires for break.
4. Please indicate the correct sequence of action to take place in an alarm/monitoring and safety system.
Alarm, st.by start, slowdown. Shutdown
5. What is an A/D and a D/A converter?
A converter that converts an analogue signal to a digital signal and vice versa.
6. Which of the 3 alternatives below is giving an OR-function?
Figure 2.
7. What is an I/P Transducer?
A transducer that converts a known electric current to a pressure proportional to the current.
8. Which of the 3 alternatives given is correct for a NOT-gate?
Figure 1.
9. Which of the 3 alternatives given is correct for an AND-gate?
Figure 3.
10. When calibrating an pressure transducer we have to adjust both SPAN and ZERO. Please indicate in which order these adjustments should be done.
First Zero adjustment and the Span adjustment. Then Zero should be rechecked.
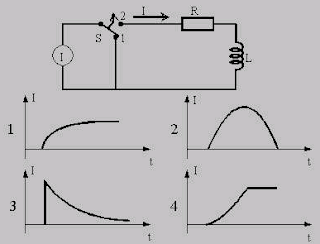
11. In a PID controller we have possibility to change the setting of the Proportional band (P), the Reset time (1) and the Rate time (D). Please indicate which curve shows the typical response to change in demand if the setting of the proportional band is too wide.
Figure 1.
12. In a PID controller we have possibility to change the setting of the Proportional band (P), the Reset time (I) and the Rate time (D). Please indicate which curve shows the typical response to change in demand if the setting of the reset time is too fast.
Figure 3.
13. n a PID controller we have possibility to change the setting of the Proportional band (P), the Reset time (I) and the Rate time (D). Please indicate which curve shows the typical response to change in demand if the setting of the rate time is too short.
Figure 2.
14. Earthing of signal cables. Which of the 4 alternatives is correct for a cable for analogue signals?
Figure 1.
15. In a fresh water tank with a height of 5 meters we shall use a pressure transmitter for level measurement. The tank has a vent-pipe leading to deck 8 meters above the top of the tank. What pressure shall we use as a guidance when ordering the pressure transducer?
1,3 Bar.
16. In a fresh water tank we are using a pressure transmitter with a range of 0-0.5 bar / 4-20mA for level measurement. The transmitter is for different reasons installed 30 centimeters from the bottom of the tank, and the tank is 5 meters high. What will the output from the transmitter be when the tank is full? (Pending no calibration is made)
18,8 mA.
17. In a fresh water tank we are using a pressure transmitter with a range of 0-0.5 bar/4-20mA for level measurement.The transmitter is for different reasons installed 30 centimeters from the bottom of the tank,and the tank is 5 meters high. What will the output from the transmitter be when the tank is empty?
4 mA.
18. What is the signal we measure out from a NiCr/Ni thermocouple?
mV.
19. In connection with exhausts gas measurement with a thermocouple we are normally using an amplifier which gives a mA-signal out. Why is this done?
The signal out from a thermocouple is mV,and can not be transferred over any longer distance without loss of voltage, giving a very bad accuracy.
20. Which of the 4 alternatives shows a PNP transistor?
Figure 2.
21. Which of the 4 alternatives shows a NPN transistor?
Figure 3.
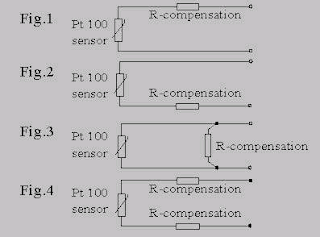
22. Due to the relative low resistance of a Pt 100 sensor we might have to compensate for the cable-resistance to ensure a correct reading. Which of the 4 alternatives given is correct for the connection of this compensation resistance.
Figure 3.
23. When the cable length from the temperature sensor to the place where we want to read the temperature exceeds approx. 10 meters we normally have to, in case of a Pt 100, in some way compensate for the cable resistance. Do we also have to do this if we choose to use a T802 temperature sensor?
No
24. Some equipment may be marked with the following symbol: What does that mean?
Intrinsically safe.
25. In installations of INTRINSICALLY SAFE equipment it is required that all equipment should be separated from non-intrinsically safe equipment, and to be of a special colour. What colour is that?
Blue
26. What is this?
A zener barrier. (Positive)
27. What is a ZENER BARRIER?
A zener barrier is a unit made to obtain intrinsically safety in installations for instrumentation in hazardous areas.
28. Can a ZENER BARRIER be installed in an hazardous area?
No, as only the output from the barrier is intrinsically safe this is not allowed.
29. What is the difference between a THERMOSTAT and a TEMPERATURE TRANSMITTER, if any?
The thermostat has one or more contacts (open or closed) depending on the temperature/setting. The temperature transmitter converts a temperature signal to an electric signal.
30. What is the difference between a PRESSURE SWITCH and a PRESSURE TRANSMITTER, if any?
The pressure switch has contact(s) that will change between open and closed position.The pressure transmitter converts a pressure signal into an electric signal.
31. What is the symbol for a THYRISTOR?
Figure 2.
32. What is the definition of DEAD BAND?
The change needed in the input signal to produce a change in the output signal.
33. What is an analogous signal?
A variable electric signal.
34. What is digital signal?
A signal representing 0 = "low" and 1 = "High"
35. What is Hz the abbreviation for?
Frequency in an Alternating Current (AC)
36. P = U x I x Root of 3) x cos (fi) What is the formula for I ?
Formula 1
37. Which alternative is correct for measuring current over the load L?
Figure 3.
38. Temperature sensors may be marked Pt 100. What does it mean?
100 ohm at 0° C
39. Temperature sensors may be marked T 802. What does it mean?
802 ohm at 20° C
40. What is the most common signal from an I/P converter?
4-20mA/3-15 PSI
41. Which method is best for determining earth failure on a 24 VDC power supply?
A lamp, (0-50 mA) and a mA-meter in series.
42. Which statement is correct with regards to power supply for equipment supplied through Zener-barriers?
The 0-voltage must always be grounded.
EXAMINATION : ELECTRO
1. Choose the group of electrical power supplies that best fits the identification of "Mains"
No. 1 diesel and No. 2 diesel
2. Which group of electrical services are likely to be supplied from an emergency generator?
Steering gear and alarm system
3. After main power is restored, a timed sequential restart of motor-driven auxilliaries is necessary to avoid:
Generator overload due to many motors starting at simultaneously
4. Choose the group of electrical power supplies that best fits the identification of "Emergency"
Emergency diesel and batteries
5. An electrical power emergency source in a ship is required because:
It satisfies the SOLAS requirements for ship safety
6. When a blackout occurs: what should be your first reaction?
Inform the bridge about the reason for blackout, and expected time to restart.
7. A 3-phase induction motor is rated at 200 A.Its initial direct- on-line starting current will be approximately:
1000 A
8. The earth lamps in a 3-phase system indicate as follows: Red= bright Yellow= dark Blue= dim
no fault - hard earth - light earth
9. An earth fault exists on the blue line of a 100 A bilge pump circuit. A second earth fault occurs on the yellow line of a 10 A ventilation fan circuit. The likely outcome is that:
A short circuit occurs between earth faults and the ventilation fan fuse blows
10. A ships 3 - phase a.c. circuit has 440 V and 220 V transformer linked sections. The effect of a single earth fault on a 220 V line will cause the following earth lamp indication:
In 440 V section: Two lamps bright. In 220 V section: Two lamps bright.
11. The insulation resistance (IR) to earth of a new galley hot-plate is measured to be 30 Mohm. When three identical hot-plates are tested together their combined IR will be:
10 Mohm
12. A motor is protected by a thermal overcurrent relay. After tripping on overload it will not be possible to reset the overcurrent relay because the:
Bimetallic strips need time to cool down
13. A 3-phase A.C. induction motor is running normally at its rated current of 150 A when a single phasing fault (open circuit) occurs in one line. The likely outcome will be:
Line currents: 0 A, 180 A, 180 A. Trip condition: trip on overload.
14. The function of the fuses in a motor starter circuit is to provide:
Short circuit protection.
15. "Protective discrimination" means the progressive grading of sizes/tripping times of:
Line fuses and overcurrent relays
16. If the A.C. line current in a generator is doubled, the heating effect in the stator windings will:
Quadruple
17. When a large motor load suddenly is disconnected from the switchboard and the genarator is AVR controlled, the voltage will:
Initially rise, then reset to the set value.
18. Under normal conditions, the electric power for services supplied from the emergency switchboard is supplied from:
The main diesel generator or shaft generator.
19. Regular (at least weekly) testing of the emergency generator must be performed to check:
Its readiness to perform as specified.
20. Unloading a generator, it is necessary to gradually decrease the load in order to avoid:
Undue overspeeding.
21. The internal e.m.f. generated in the phase windings of an a.c. generator is controlled by:
The diesel speed and excitation current.
22. A 10% reduction in generator speed occurs due to a faulty governor. The likely consequence for each motor powered from this generator is to:
Reduce motor speed by about 10%
23. The pair of instruments necessary for generator synchronising are:
Voltmeter and synchroscope
24. Prior to synchronising, the generator voltage and frequency are respectively controlled by:
AVR and speed governor
25. For ideal synchronising, the phase angle difference between the incomer e.m.f. and the busbar voltage should be:
0°
26. During synchronising, the incoming generator should be running slightly "fast" compared to the busbar frequency.This is to ensure that the:
Incomer picks up as a generator
27. The correct time to synchronise is usually taken to be when the synchroscope reaches the "5 to 12" position. This to allow for:
Circuit breaker operating time
28. After successful synchronising the kW and kVar loading are respectively transfered by the following controls:
Speed governor and voltage regulator
29. For two generators running in parallel, their share of additional load (kW) will be determined by the:
Governor droop settings on each prime mover
30. Generator 1 and 2 are working in parallel. Prime-mover 2 suffers a total fuel loss. The likely outcome is:
No.2 generator trips on reverse power
31. It is possible to operate two similar generators in parallel at equal power (kW) but at different power factors. The generator with lower power factor will cause it to run:
Hotter due to increased current
32. Check-synchroniser equipment is often installed to:
Prevent manual synchronising outside permitted limits
No. 1 diesel and No. 2 diesel
2. Which group of electrical services are likely to be supplied from an emergency generator?
Steering gear and alarm system
3. After main power is restored, a timed sequential restart of motor-driven auxilliaries is necessary to avoid:
Generator overload due to many motors starting at simultaneously
4. Choose the group of electrical power supplies that best fits the identification of "Emergency"
Emergency diesel and batteries
5. An electrical power emergency source in a ship is required because:
It satisfies the SOLAS requirements for ship safety
6. When a blackout occurs: what should be your first reaction?
Inform the bridge about the reason for blackout, and expected time to restart.
7. A 3-phase induction motor is rated at 200 A.Its initial direct- on-line starting current will be approximately:
1000 A
8. The earth lamps in a 3-phase system indicate as follows: Red= bright Yellow= dark Blue= dim
no fault - hard earth - light earth
9. An earth fault exists on the blue line of a 100 A bilge pump circuit. A second earth fault occurs on the yellow line of a 10 A ventilation fan circuit. The likely outcome is that:
A short circuit occurs between earth faults and the ventilation fan fuse blows
10. A ships 3 - phase a.c. circuit has 440 V and 220 V transformer linked sections. The effect of a single earth fault on a 220 V line will cause the following earth lamp indication:
In 440 V section: Two lamps bright. In 220 V section: Two lamps bright.
11. The insulation resistance (IR) to earth of a new galley hot-plate is measured to be 30 Mohm. When three identical hot-plates are tested together their combined IR will be:
10 Mohm
12. A motor is protected by a thermal overcurrent relay. After tripping on overload it will not be possible to reset the overcurrent relay because the:
Bimetallic strips need time to cool down
13. A 3-phase A.C. induction motor is running normally at its rated current of 150 A when a single phasing fault (open circuit) occurs in one line. The likely outcome will be:
Line currents: 0 A, 180 A, 180 A. Trip condition: trip on overload.
14. The function of the fuses in a motor starter circuit is to provide:
Short circuit protection.
15. "Protective discrimination" means the progressive grading of sizes/tripping times of:
Line fuses and overcurrent relays
16. If the A.C. line current in a generator is doubled, the heating effect in the stator windings will:
Quadruple
17. When a large motor load suddenly is disconnected from the switchboard and the genarator is AVR controlled, the voltage will:
Initially rise, then reset to the set value.
18. Under normal conditions, the electric power for services supplied from the emergency switchboard is supplied from:
The main diesel generator or shaft generator.
19. Regular (at least weekly) testing of the emergency generator must be performed to check:
Its readiness to perform as specified.
20. Unloading a generator, it is necessary to gradually decrease the load in order to avoid:
Undue overspeeding.
21. The internal e.m.f. generated in the phase windings of an a.c. generator is controlled by:
The diesel speed and excitation current.
22. A 10% reduction in generator speed occurs due to a faulty governor. The likely consequence for each motor powered from this generator is to:
Reduce motor speed by about 10%
23. The pair of instruments necessary for generator synchronising are:
Voltmeter and synchroscope
24. Prior to synchronising, the generator voltage and frequency are respectively controlled by:
AVR and speed governor
25. For ideal synchronising, the phase angle difference between the incomer e.m.f. and the busbar voltage should be:
0°
26. During synchronising, the incoming generator should be running slightly "fast" compared to the busbar frequency.This is to ensure that the:
Incomer picks up as a generator
27. The correct time to synchronise is usually taken to be when the synchroscope reaches the "5 to 12" position. This to allow for:
Circuit breaker operating time
28. After successful synchronising the kW and kVar loading are respectively transfered by the following controls:
Speed governor and voltage regulator
29. For two generators running in parallel, their share of additional load (kW) will be determined by the:
Governor droop settings on each prime mover
30. Generator 1 and 2 are working in parallel. Prime-mover 2 suffers a total fuel loss. The likely outcome is:
No.2 generator trips on reverse power
31. It is possible to operate two similar generators in parallel at equal power (kW) but at different power factors. The generator with lower power factor will cause it to run:
Hotter due to increased current
32. Check-synchroniser equipment is often installed to:
Prevent manual synchronising outside permitted limits
Sabtu, 18 Februari 2017
EXAMINATION : ELECTRONICS
1. What is the resistance value of this resistor:
10 k ohm
2. This resistor has the value of 68 k ohm. Which color code will you put on the different color-rings:
blue , gray , orange
3. Which electronic component is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Resistance, 3300 ohms
4. Which electronic component is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Capacitor
5. Which electronic component is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Potentiometer, 10 kilo-ohms
6. Which electronic component is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Transistor
7. Which electronic component is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Zener diode
8. Which electronic component or system of components is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Operational amplifier
9. Which electronic component or system of components is this graphical symbol illustrating:
Bandpass filter
10. Which electronic component or system of components is this graphical symbol illustrating ?
Inverter
11. The figures show a graphical symbol for a particular electronic component and a typical working characteristic for the same component. Which component?
Silicon controlled rectifier (SCR)
12. The figures show a graphical symbol for a particular electronic component and a typical working characteristic for the same component. Which component?
Triac
13. The figure shows a silicon controlled rectifier with a RC circuit connected in parallel. RC circuit is often used in such connection. For which purpose?
Protect the SCR against damage caused by high voltage spikes
14. The figures show a graphical symbol for a particular electronic component and a typical working characteristic for the same. Which component?
Transistor
15. The circuit symbol is a driver for a solenoid (coil) of a solenoid valve S. What is the purpose of the diode IN 4002 connected in parallel to the solenoid S?
Blocking inductive kick from the solenoid
16. This is a typical emitter follower. What is the main benefit obtained by use of an emitter follower?
The input impedance is made much larger than the output impedance
17. Ordinary thyristors (SCR) must often be protected against reverse overvoltage transients because even over-voltages of extremely short duration can destroy them. These circuits have been given such over-voltage protection, but only one of them is correct. Which?
Figure 1
18. Diodes are widely used in rectification, or the conversion of alternating current to direct current. This circuit symbol is such example. The input voltage V(in) is sine-wave AC. Which of the shown output voltages is correct for this circuit?
Figure 1
19. The circuit symbol is a widely used system for rectification of AC into DC. Which of the diagrams is the correct for the out- put voltage when the input voltage is sine-shaped as shown?
Figure 1
20. The circuit symbol is a widely used system for converting AC voltage to DC voltage. In this case the input voltage is a sine-wave. Which of the shown diagrams is correct for the output voltage V(out.)
Figure 1
21. The circuit symbol is a full-wave bridge rectifier. Which electronic component will you connect between 'a' and 'b' in order to obtain reduced ripple voltage to the load RL.
Capacitor
22. This amplifier circuit is a very common configuration used to amplify the difference in voltage between two input signals; in this case input 1 and 2. What is this amplifier called?
Differential amplifier
23. Which function is this operational amplifier circuit performing?
Differentiator
24. Which function is this operational amplifier circuit performing?
Integrator
25. Which function is this operational amplifier circuit performing?
Non-inverting amplifier
26. Which function is this operational amplifier circuit performing?
Inverting amplifier
27. These circuits are all active filters. Which of the circuits is a high-pass filter?
Figure 1
28. These circuits are all active filters. Which of the circuits is a low-pass filter?
Figure 2
29. These circuits are all active filters. Which of the circuits is a band-pass filter?
Figure 3
30. An important quantity which is useful in circuit analysis is known as conductance G (Siemens). Which of the formulas A to D expresses the conductance for this circuit?
G = I / R
31. There are two fundamental laws of electric circuits.
The first states that the amount of direct current flowing away from a point in a circuit is equal to the amount flowing to that point.
The second is a confirmation of the principle of the conservation of energy and says "The difference in electrical potential between any two points is the same regardless of the path along which it is measured".
Whose laws are they?
Kirchoff's
32. Use Kirchoff's current law and Ohm's law to calculate the value of the current I for this circuit.
22 A
33. Use Kirchoff's voltage law and Ohm's law to calculate the voltage V(2) across the resistance R(2).
4,5 V
34. Find the value of the voltage drop from terminal A to terminal B in this circuit:
- 38 V
35. This circuit consists of two resistances, R1 = 6 ohm and R2 = 12 ohm , connected in series. Calculate the equivalent resistance R(S) of the two resistances.
R(S) =18 ohm
36. Choose the resistance R from the list A to D which allows highest possible current without exceeding 5W power consumption.
R(S) = 25 ohm
37. This circuit consists of two resistances, R(1)= 12 ohm and R(2) = 6 ohm, connected in parallel. Calculate the equivalent value R(S) of the two resistances.
R(S)= 4 ohm
38. This circuit consists of two capacitors, C(1) = 6 µF and C(2) = 12 µF, in series. Calculate the equivalent C(S) of the two capcitors.
C(S) = 4 µF
39. The circuit consists of two capacitors, C(1) = 6 µF and C(2) = 12 µF, in parallel. Calculate the equivalent C(S) of the two capacitors.
C(S) = 18 µF
40. The circuit consists of two inductors, L(1) = 6 H and L(2) = 12 H, in series. Calculate the equivalent L(S) of the inductors.
L(S) = 18 H
41. The circuit consists of two inductors, L(1) = 6 H and L(2) = 12H, connected in parallel. Calculate the equivalent L(S) of the two inductors.
L(S) = 4 H
42. This circuit consists of a voltage source V, a change-over switch S, a resistor R and a capacitor C. The voltage/time figures 1 to 4 show possible changes in the voltage V(C) in case the switch S is suddenly shifted from position 1 to 2 at time t = 0. Only one of the diagrams is correct. Which?
Figure 1
43. This circuit consists of a current source I, a change-over switch S, a resistor R and a capacitor C. The current/time figures 1 to 4 show possible changes in the current I in case the switch S is suddenly shifted from position 1 to 2 at time t= 0. Only one of the diagrams is correct. Which?
Figure 1
44. This circuit consists of a voltage source V, a change-over switch S, a resistor R and an inductor L. The voltage/time figures 1 to 4 show possible changes in the voltage V(L) in case the switch S is suddenly shifted from position 1 to 2 at time t = 0. Only one of the diagrams is correct. Which?
Figure 1
45. This circuit consists of a current source I, a change-over switch S, a resistor R and an inductor L. The voltage/time figures 1 to 4 show possible changes through L if the switch S is suddenly shifted from position 1 to 2 at time t = 0. Only one of the diagrams is correct. Which?
Figure 3
46. Wheatstone resistance bridge is often used for measuring resistances in for instance Pt 100 temperature sensors or strain gauges. This figure is such a bridge. What is the requirement for balance of such a bridge. i.e. the current through the meter i(m) = 0.
R1 / R2 = R3 / R4
47. This is a parallel L-C circuit with curve showing frequency- impedance characteristics. Which of the formulas A to D will you utilize for determining the resonant frequency f?
f o = 1 / (2 sqrt (L/C) )
48. Which function is this circuit performing?
Differentiating
49. There are many applications in circuit theory where it is important to obtain the maximum possible power that a given source can deliver. This figure consists of a practical voltage source V(g) with internal resistance R(s). A resistance R(L) will maximize the power transmission from the source to R(L)?
R(L) = R(s)
50. This circuit is a transformer with two windings, N(1) = 2000 and N(2) = 1000 turns, on a common magnetic circuit. Assume that there are no energy losses in the transformer itself. Calculate the output voltage V(2) when the input voltage is V(1) = 100 Volt.
V(2) = 50 V
51. This figure is a transformer, with two windings, N(1) = 2000 and N(2) = 1000 turns, on a common magnetic circuit. Assume that there is no energy loss in the transformer itself. Calculate the current I(2) when the current I(1) = 2 A.
I(2) = 4 A
52. A transformer with 10:1 turns ratio and rated 50 kVA, 2400/240 Volts, 60 Hz, is used to step down the voltage to a distribution system. The low tension voltage is to be kept constant at 240 Volts. What load impedance connected to the low-tension side will cause the transformer to be fully loaded?
1.15 Ohms
53. This circuit is a logic gate with two input signals, A and B, and one output signal Q. Which type of logic function is the gate giving?
OR gate
54. This circuit is a logic gate with two input signals, A and B, and one output signal Q. Which type of logic function is the gate giving?
NOR gate
55. This circuit is a flip-flop. Which type?
Bi-stable flip-flop
56. This graphical symbol is a logic gate. Which gate?
NOR
57. This graphical symbol is a logic gate. Which gate?
NAND
58. This graphical symbol is a logic gate. Which gate?
AND
59. This graphical symbol is a logic gate. Which gate?
OR
60. Transmission lines play a central role in radio frequency circuits, where they are used to pipe signals around from one place to another within a circuit, and often to an antenna system. General rules for such transmission line is that they must be "matched". Which of the cables below would you use to obtain a matched transmission between Z1 and Z2?
Figure 4
61. Radio frequency signals can carry information from one place to another if it is modulated. There are several ways to modulate a carrier. Which modulating method is illustrated here?
Amplitude modulation (AM)
62. Which cell voltage will you supply for trickle charging of a lead acid battery?
2.15 V
63. What kind of electrolyte is used for Nickel-iron batteries?
Solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) and water
64. How can we check if a lead-acid type battery is fully charged or not?
Measure the specific gravity of the electrolyte
65. When data are to be transferred over telephone lines, we often utilize modem at each end. Which of the following adapter cards (parts) will you use for interfacing a modem to a computer?
Serial adapter
66. The powersupply to the harddisk of a personal computer consists normally of two voltages. Which?
5 V and 12 V
67. The picture shows a common used 3,5 inches diskette type for storing data. What is the data storing capacity for such diskette?
1.44 MB
68. What do you understand with a computer's POST system?
A series of tests run by the computer at power on
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)